In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, organizations are increasingly recognizing the value of data-driven insights. However, to harness the full potential of these insights, proper solutions must be in place to connect, transport, and process data efficiently. This is particularly critical in mission-critical applications, where the need for secure, fast, reliable, and accurate results is paramount. Modern Industrial Edge Solutions present a transformative approach that promises to revolutionize data handling in such industrial environments.
What Are Industrial Edge Solutions?
The term “edge” in Industrial Edge Solutions or Edge Computing refers to the location where computational activity takes place. Traditionally, data processing has relied on cloud computing, which involves sending data to remote data centers. In contrast, edge computing occurs at the periphery of the network, close to where data is generated. This shift reduces latency, costs, and security risks associated with transmitting data to distant servers.
In industrial settings, the "industrial edge" is the local deployment of data-handling activities and network operations. This typically involves hardware components such as computers, controllers, and sensors within the automation pyramid. The proximity of the edge to the data source is crucial for applications requiring real-time decision-making, enhanced security, and high reliability.
Edge computing, therefore, describes the data processing that happens at these edge locations. When applied to industrial environments, this is known as "industrial edge computing." By bringing computational processes closer to data-generating devices, industrial edge computing minimizes the reliance on cloud and enterprise systems, leading to faster and more efficient operations. When combined with edge applications and complementary services, this setup forms an "industrial edge solution."
Types of Industrial Edge Solutions?
As per IOT Analytics, Industrial Edge Solutions are build on Edge to process data closer to where it is generated, rather than relying solely on centralized cloud computing.
These solutions can be categorized into three types: Thick Edge, Thin Edge, and Micro Edge.
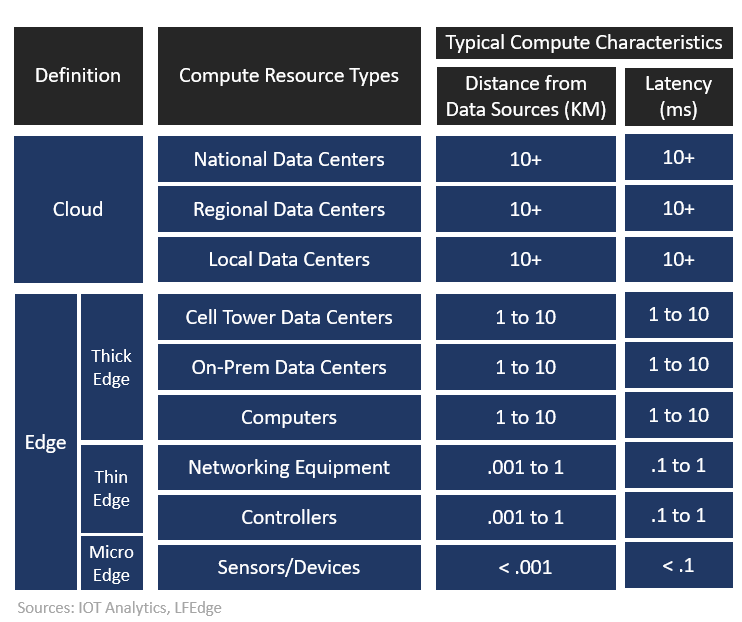
- Thick Edge:
- Definition: Thick Edge devices are equipped with substantial computational power and storage capabilities, allowing them to perform complex data processing and analytics tasks independently.
- Characteristics: These devices can handle large volumes of data, execute machine learning algorithms, and make real-time decisions without constant connectivity to the cloud.
- Use Cases: Thick Edge solutions are ideal for industries requiring high-performance processing, such as manufacturing, where real-time analytics and low latency are crucial for operations.
- Thin Edge:
- Definition: Thin Edge devices have more limited processing and storage capacities compared to Thick Edge devices. They are designed to perform basic data filtering, aggregation, and simple analytics tasks.
- Characteristics: Thin Edge devices primarily serve as intermediaries between sensors/actuators and more powerful processing units (either Thick Edge devices or cloud servers). They help in reducing the data load by pre-processing and only sending essential information for further analysis.
- Use Cases: Thin Edge solutions are commonly used in scenarios where data needs to be collected from multiple sources and pre-processed before being transmitted to higher-capacity systems for detailed analysis, such as in smart agriculture or building management systems.
- Micro Edge:
- Definition: Micro Edge devices are the simplest and most resource-constrained among the three types. They focus on collecting data from sensors and transmitting it with minimal processing.
- Characteristics: These devices perform very basic tasks like data acquisition, simple filtering, and temporary storage. They are optimized for low power consumption and often operate on battery power.
- Use Cases: Micro Edge solutions are suited for applications where lightweight, low-cost, and low-power devices are needed, such as in environmental monitoring, wearable technology, or small-scale IoT deployments.
These three types of Industrial Edge Solutions provide a spectrum of capabilities, enabling organizations to choose the appropriate level of edge computing power based on their specific application needs and operational requirements.
Why Are Industrial Edge Solutions Necessary?
The necessity of industrial edge solutions is underscored by their ability to process data locally, offering expedited, reliable, and secure insights. This capability has become a fundamental tool for realizing the potential of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and Industry 4.0.
Several technological trends have contributed to the rise and significance of industrial edge solutions:
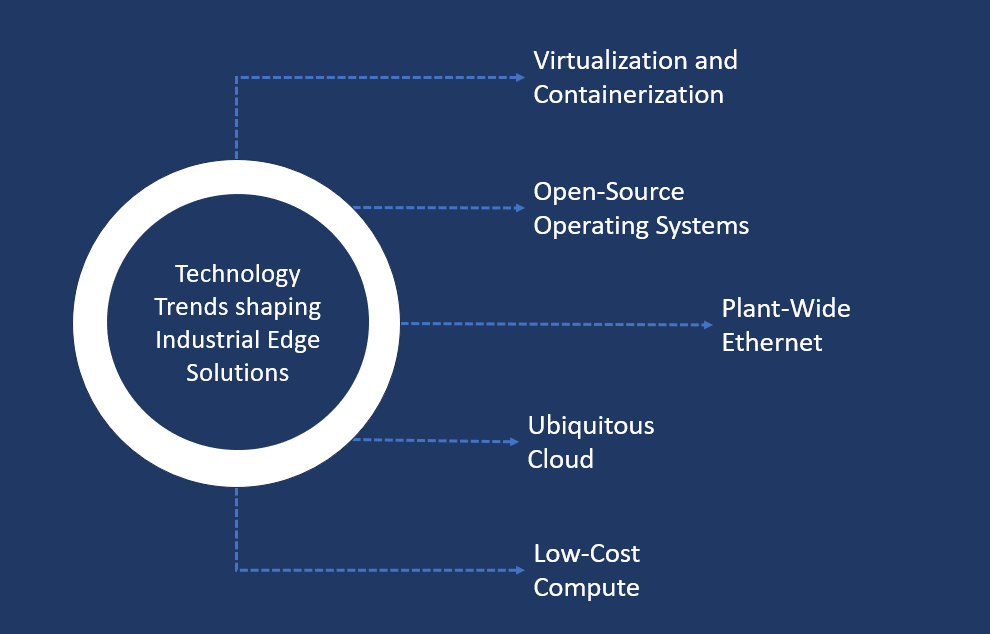
- Virtualization and Containerization: These technologies allow applications to be packaged and deployed efficiently, making it easier to manage and scale workloads.
- Open-Source Operating Systems: The use of open-source platforms accelerates the development of new applications while reducing costs.
- Plant-Wide Ethernet: Enhanced bandwidth availability and faster transmission speeds facilitate better connectivity within industrial networks.
- Ubiquitous Cloud: Constant connectivity ensures seamless integration between local and remote computing resources.
- Low-Cost Compute: Advances in processing power coupled with decreasing CPU costs enable more workloads to be handled on fewer devices.
Importance of Industrial Edge Solutions
The trends described above collectively enhance the value of Industrial Edge Solutions, allowing organizations to design systems with higher computing power capable of running numerous workloads at lower costs. An Industrial Ethernet network, essential for deploying industrial edge solutions, supports these capabilities. By processing data locally instead of offsite or in the cloud, organizations can achieve several critical objectives:
- Hardware-Agnostic Applications: Historically, workloads were limited to specific hardware. However, with virtualization and containerization, workloads can now be deployed as applications on industrial edge computing platforms, providing greater flexibility and scalability.
- Flexible Architecture: The increasing complexity of workloads in industrial environments necessitates a flexible architecture. Industrial edge solutions enable organizations to run these complex workloads closer to the data source, ensuring real-time processing and decision-making. Secure and reliable industrial networks are essential for transporting data effectively between IT and OT systems.
- Cost Reduction: In the pursuit of cost efficiency, organizations are scrutinizing their industrial operations. The ability to deploy low-cost, high-power computing reduces the need for extensive hardware installations. Additionally, processing workloads on premises through industrial edge solutions minimizes the costs associated with data transmission, storage, and cloud processing.
Conclusion
Industrial edge solutions represent a significant advancement in the way data is handled in industrial environments. By leveraging edge computing, organizations can achieve faster, more secure, and cost-effective data processing, driving the realization of IIoT and Industry 4.0 use cases. As technological trends continue to evolve, the value and importance of industrial edge solutions will only grow, offering organizations the tools they need to stay competitive in an increasingly data-driven world.