What Is Edge Computing
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computational resources, data storage and decision making closer to the location where it is needed, rather than relying on a centralized cloud-based systems.
In traditional cloud computing, data is sent to a remote server for processing, and the results are then sent back to the user. Edge computing, on the other hand, processes data on local devices or nearby edge servers, reducing latency and increasing efficient and faster decision making.
As organizations increasingly demand real-time insights, ultra-low latency, and resilient distributed systems, Edge Computing is becoming mission-critical.
To help professionals move confidently from concepts to execution, our course “Edge Computing Essentials: Concepts to Real-World Use Cases” provides a structured, hands-on learning path covering core principles, architecture, platforms, and enabling technologies—directly mapped to real-world industrial use cases.
If you’re looking to build in-demand skills and accelerate your career in Edge Computing, this is the right place to start.
Key features of edge computing
- Low Latency: Many modern applications like Autonomous Vehicles, Industrial Automation, and Augmented Reality (AR) require lower latency (typically less than 20ms) and decision making. By processing data closer to the source, edge computing reduces the time it takes for data to travel from the source to the processing location and back, thus enabling faster local decision making.
- Bandwidth Efficiency: Edge computing helps in reducing the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to the cloud, as only relevant or processed information is sent. This is beneficial in scenarios where bandwidth is limited or costly.
- Improved Privacy and Security: Cybersecurity is a very big concern today. Edge computing enhances privacy and security by processing sensitive data locally rather than sending it to a centralized cloud. This is particularly important in applications like healthcare.
- Decentralized Architecture: Edge computing employs a decentralized architecture where processing can happen at various points in the network. It can happen on the Device, On the Smart Device Edge, On the Regional/Telco Edge etc.
- Real-time Processing: The ability to process data at or near the source enables real-time analytics and decision-making, which is crucial for applications requiring instant responses.
- Scalability: Edge computing systems can be scaled by adding more edge devices to the network.
- Cost Efficiency: Edge computing can be more cost-effective than traditional cloud computing for certain applications, as it minimizes the need for expensive, high-bandwidth connections to central data centers.
- Offline Operation: Edge devices can continue to function even when disconnected from the central cloud. This is particularly beneficial in scenarios where continuous internet connectivity cannot be guaranteed.
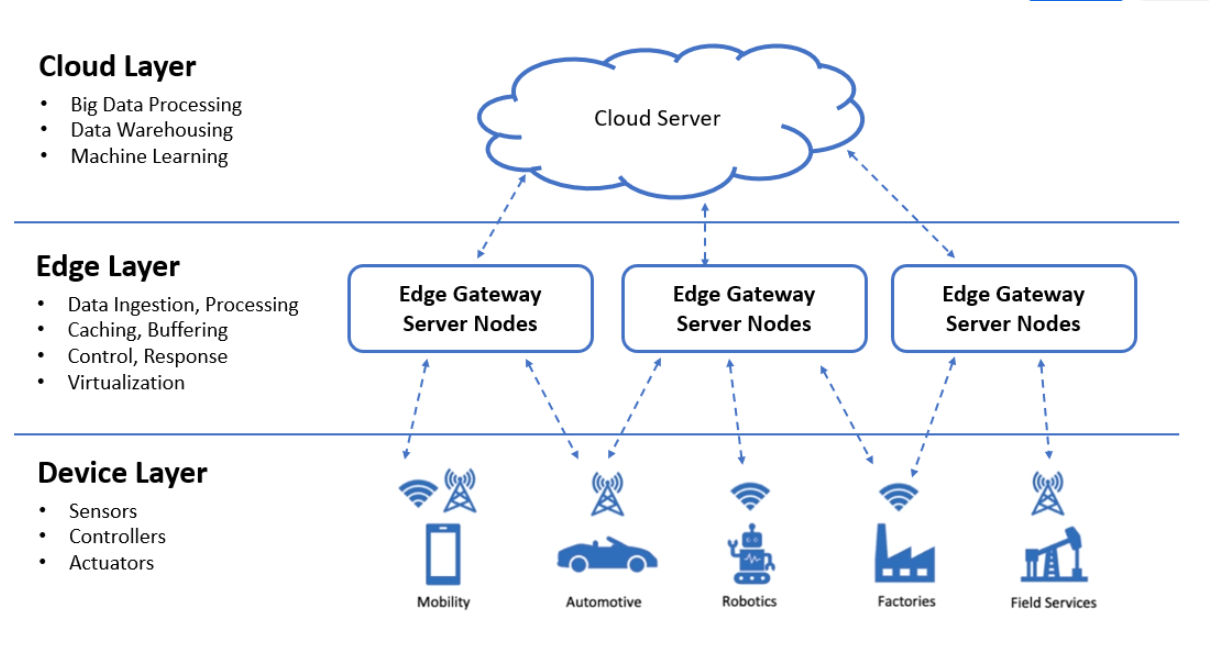
Basic Architecture of Edge Computing
Modern Application areas of Edge Computing
Edge Computing is important for all the application areas which need real-time or near real time processing, response and actions along with need to run heavy workloads like Analytics & Inferencing.
It is also important in applications where processing and decision making can be done locally rather than sending the information to the Cloud for cost and latency reasons.
As organizations increasingly demand real-time insights, ultra-low latency, and resilient distributed systems, Edge Computing is becoming mission-critical.
To help professionals move confidently from concepts to execution, our course “Edge Computing Essentials: Concepts to Real-World Use Cases” provides a structured, hands-on learning path covering core principles, architecture, platforms, and enabling technologies—directly mapped to real-world industrial use cases.
If you’re looking to build in-demand skills and accelerate your career in Edge Computing, this is the right place to start.
Following are some of the modern application areas of edge computing:
- Internet of Things (IoT): Edge computing is integral to IoT, where a multitude of devices generate and process data. It enables quick and efficient decision-making at the device level.
- Industrial Automation: In manufacturing and industrial settings, edge computing is allowing for real-time monitoring and control of processes, improving efficiency and reducing downtime.
- Industrial IOT: Industrial IOT companies are further expanding into Edge Computing for running application like Analytics and Inferencing on the Edge, while Machine Learning is happening on Cloud.
- Smart Cities: Edge computing supports applications such as traffic management, public safety, and environmental monitoring in smart city initiatives.
- Healthcare: Edge computing is used for real-time monitoring of patients, processing medical imaging data, and ensuring data privacy in healthcare applications.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): Edge computing helps reduce latency in AR and VR applications, providing a more immersive and responsive user experience.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Edge computing plays a crucial role in autonomous vehicles by enabling real-time data processing for tasks such as object recognition, decision-making, and navigation. This helps enhance the safety and efficiency of autonomous driving systems.
- Retail: In retail environments, edge computing can be used for in-store analytics, inventory management, and personalized customer experiences. It allows retailers to analyze customer behavior in real time, optimize pricing strategies, and streamline supply chain operations.
- Agriculture: Edge computing in agriculture involves the use of sensors and devices to monitor soil conditions, crop health, and weather patterns. Real-time analysis at the edge can help farmers make data-driven decisions, optimize irrigation, and enhance crop yields.
- Energy Management: Edge computing is employed in smart grids and energy management systems to monitor and control energy distribution. It facilitates real-time analysis of energy consumption patterns, predictive maintenance for equipment, and optimization of energy efficiency.
- Logistics and Supply Chain: In logistics and supply chain management, edge computing supports real-time tracking of shipments, inventory management, and route optimization. This improves the overall efficiency of supply chain operations and reduces delays.
- Video Surveillance & Analytics: High Definition Video data is typically very large in size (10s of Mbps). Its very expensive to send this data to the cloud and do Analytics. Edge computing helps to process and analyze video these video feeds locally.
- Telecommunications: Telco Edge Networks and Edge Computing Infrastructure is increasingly being integrated into 5G networks to reduce latency and enhance the performance of communication services. Private 5G around Edge computing is evolving as very strong use case for all kinds of application like augmented reality, virtual reality, and online gaming.
- Finance: In the financial industry, edge computing supports real-time fraud detection, risk analysis, and algorithmic trading. It enhances the security and speed of financial transactions and allows for quicker decision-making based on market data.
- Edge AI Applications: Edge computing is closely tied to artificial intelligence (AI) at the edge. Applications include real-time image recognition, natural language processing, and machine learning on devices like cameras, drones, and sensors without the need for constant cloud connectivity.
As organizations increasingly demand real-time insights, ultra-low latency, and resilient distributed systems, Edge Computing is becoming mission-critical.
To help professionals move confidently from concepts to execution, our course “Edge Computing Essentials: Concepts to Real-World Use Cases” provides a structured, hands-on learning path covering core principles, architecture, platforms, and enabling technologies—directly mapped to real-world industrial use cases.
If you’re looking to build in-demand skills and accelerate your career in Edge Computing, this is the right place to start.